Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a complex mental health condition that can significantly impair an individual’s daily life. Defined by the DSM-V (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition) as a psychiatric disorder that can occur in people who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event, PTSD manifests through various symptoms, including intrusive memories, avoidance behaviors, negative changes in thinking and mood, and hyperarousal. The diagnosis of PTSD requires exposure to a traumatic event, either directly experiencing it, witnessing it, or learning about it occurring to a close family member or friend, with subsequent symptoms persisting for more than a month.
Assessment of PTSD
Assessing PTSD typically involves the use of standardized measures like the PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), which evaluates the severity of PTSD symptoms based on the DSM-V criteria. This assessment tool helps clinicians understand the extent of a patient’s PTSD symptoms, aiding in treatment planning and monitoring progress over time.
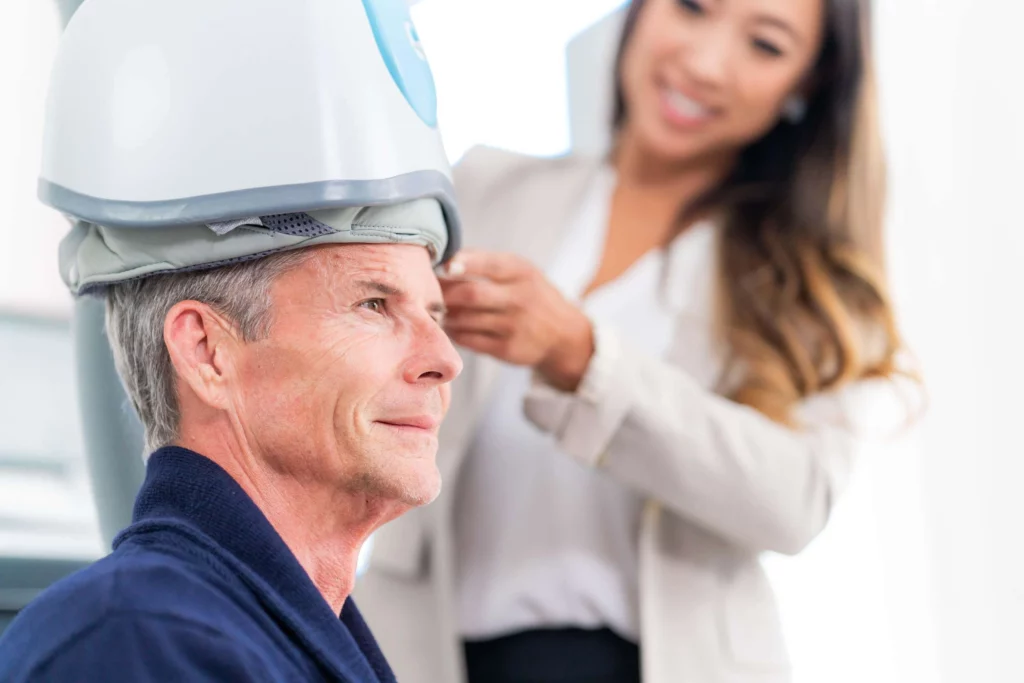
Traditionally, PTSD treatment has encompassed psychotherapy, medication, or a combination of both. However, emerging research suggests that Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) holds promise as a non-invasive and effective alternative or adjunctive treatment for PTSD. TMS works by delivering magnetic pulses to specific regions of the brain, modulating neuronal activity and potentially alleviating symptoms associated with various psychiatric disorders, including PTSD.
Recent studies have highlighted the potential of deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (dTMS) as a novel approach to treating PTSD. Unlike conventional TMS, which targets superficial regions of the brain, dTMS can reach deeper structures associated with mood regulation and emotional processing, making it particularly suitable for addressing the underlying neural mechanisms of PTSD.
DEEP TMS
One of the most compelling aspects of dTMS with Brainsway Deep TMS for PTSD treatment is its ability to induce remission in patients who have previously been resistant to traditional interventions. In a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, researchers found that dTMS produced significant reductions in PTSD symptoms, with a substantial proportion of participants achieving full remission. This suggests that dTMS holds promise not only for symptom management but also for promoting long-term recovery in individuals with treatment-resistant PTSD.
Furthermore, dTMS has demonstrated favorable safety and tolerability profiles in clinical trials, making it a viable option for patients who may be unable to tolerate or respond to conventional pharmacotherapy. Unlike medications, which can often cause unwanted side effects or dependency issues, dTMS offers a non-pharmacological alternative that is well-tolerated and devoid of systemic effects.
The mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of dTMS in PTSD are still being elucidated, but research suggests that its ability to modulate neural circuitry involved in emotional processing and regulation plays a crucial role. By targeting specific brain regions implicated in PTSD pathophysiology, such as the prefrontal cortex and amygdala, dTMS may help restore aberrant neural connectivity and promote adaptive responses to trauma-related stimuli.
In addition to its efficacy in reducing PTSD symptoms, dTMS has been associated with improvements in comorbid conditions commonly observed in individuals with PTSD, such as depression and anxiety. This suggests that dTMS may offer a holistic approach to addressing the complex interplay of psychiatric symptoms often seen in PTSD patients, leading to more comprehensive and enduring therapeutic outcomes.
CONCLUSION
At Resiliency Mind+Body Medicine, we are utilizing our unique PTSD protocols and are seeing a reduction of PTSD symptoms in 90% of our patients. As with any emerging treatment modality, ongoing research is needed to further elucidate the optimal parameters and protocols for dTMS in PTSD treatment, and our team of experts is actively involved in a multi-site study of deep TMS. Additionally, efforts to identify biomarkers predictive of treatment response could help tailor dTMS interventions to individual patient needs, optimizing outcomes and reducing unnecessary healthcare costs.
In conclusion, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, particularly deep TMS, represents a promising avenue for the treatment of PTSD. By targeting neural circuitry implicated in the pathophysiology of PTSD, dTMS offers a non-invasive and effective therapeutic option for individuals who have not responded to conventional treatments. As research in this field continues to evolve, dTMS holds the potential to revolutionize the way we approach and manage PTSD, offering hope for a brighter future for those affected by this debilitating condition.